What is the Flow of Goods?
The flow of goods starts with sourcing raw materials and components, then goes through the manufacturing process, followed by packaging, storage, and distribution to the end user.
The manufacturing process is a part of the supply chain. It is usually considered the first step in the flow of goods, where raw materials are transformed into finished products ready for distribution and consumption.
Product vs Goods
Before we continue, you may ask yourself: is there a difference between a good and a product?
Goods and products are often used interchangeably but have slightly different meanings.
Goods refer to tangible items that can be bought and sold, such as food, clothing, furniture, and electronics. They are physical items that can be stored, transported, and consumed.
Products are a more general term that can refer to both tangible goods and intangible services. A product can be a good, such as a car, or a service, such as a haircut. Products are anything that can be offered to a market to satisfy a want or need.
In summary, goods refer to tangible items, while products can include both tangible goods and intangible services.
Mapping Your Flow
Value chain mapping or value stream mapping (VSM) and the flow of goods are related concepts in the field of supply chain management.
Value chain mapping is the process of identifying and analyzing all the activities that are involved in creating and delivering a product or service to the customer. This includes everything from the sourcing of raw materials to the distribution of the finished product. The value chain is a visual representation of these activities and the relationships between them. It helps companies to understand where they add value and where they can improve their operations.
The flow of goods refers to the movement of products from the point of origin, such as a manufacturer or supplier, to the point of consumption, such as a retail store or consumer. This includes the transportation, storage, and distribution of goods.
When creating a value chain map, the flow of goods is one of the key areas to consider. The flow of goods can be analyzed and improved to ensure that products are delivered to customers on time and at the right cost. This can be achieved by reducing unnecessary transportation, storage, and handling of goods.
By mapping the value chain and understanding the flow of goods, companies can identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and areas for improvement in their supply chain operations. This can help to reduce costs, increase efficiency, and improve customer satisfaction.
VSM and Flow of Goods
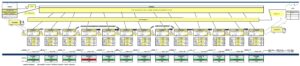
To better visualize the strength of value stream mapping, here is an example of a VSM :
We have a complete view of each operation of the production process. In one quick look, we can identify the bottlenecks, the lead time, the overall rate of return of the value chain, etc.
For an industrial engineer like me, it is simply the best tool to analyze and optimize the value chain of a business.
If you need any assistance to realize a VSM and optimize your flow, don’t hesitate to contact us.
Optimizing your Flow of Goods
Use your mapping to identify bottlenecks and improve your productivity…
Also, here are other suggestions to improve your flow of goods:
Implement a transportation management system (TMS):
A TMS can help to optimize the transportation of goods by automating the planning, execution, and monitoring of shipments. It can also help to reduce transportation costs by identifying the most cost-effective routes and carriers.
Use warehouse management systems (WMS):
A WMS can help to optimize the storage and handling of goods by automating inventory management, tracking, and reporting. This can help to reduce inventory costs and improve the accuracy of stock levels.
Implement a demand-driven approach:
By using a demand-driven approach, companies can better align their production and distribution with customer demand. This can help to reduce the risk of stockouts and overstocking and improve customer satisfaction.
Improve communication and collaboration with suppliers and partners:
By improving communication and collaboration with suppliers and partners, companies can better coordinate the flow of goods and reduce delays and errors.
Use data and analytics:
By collecting and analyzing data on the flow of goods, companies can identify trends, patterns, and areas for improvement. This can help to optimize the flow of products by making data-driven decisions.
Continuously monitor and measure:
Monitoring and measuring the flow of goods can help identify and address issues quickly. This can be done by using key performance indicators (KPIs) to track the performance of the flow of goods.
By implementing these strategies and continuously monitoring and improving the flow of goods, companies can optimize their supply chain operations, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction.
What Does a Good Flow to Your Business?
A good flow brings several advantages:
Efficiency stacks up:
By leveraging waste and enhancing the added value of our products and operations, overall plant efficiency is improved. This increases its production capacity and quality.
Reduced costs:
Reduces costs by minimizing waste and maximizing the use of resources. This can be achieved, among other things, by optimizing unnecessary transport, storage, and handling of goods.
Improved customer satisfaction:
By improving efficiency, and quality and using operations that do not add value to the products, we reduce the passage time of the parts and this makes it possible to better respond to customer requests. Especially since demand can fluctuate over time. It is therefore important to be flexible and agile. A good flow of goods achieves this flexibility and agility!
Flexibility :
As mentioned earlier, good flow allows a company to react quickly to changes in demand and adjust production and distribution accordingly. This can reduce production costs (especially start-up costs) and improve the on-time delivery rate.
Better inventory management:
Enables businesses to improve inventory tracking and management, as well as the risk of stockouts, overstocking, and inventory degradation. By improving its efficiency (reduction of transit time), flexibility, and agility, on a need for less stock to compensate for market fluctuations.
In products causing stocks, we reduce the risk of breakage during handling, expiry (obsolete products, passing fashion, expired), etc.
Best Selling and Planning:
Ultimately, a good flow of goods enables businesses to make better forecasting and planning decisions based on accurate data and trends.
By stabilizing production and using the variability of production times, on a better overview of its real production capacity. This greatly facilitates the planner’s life.
All in all, a good flow of goods can help a business be more efficient, responsive (agile), and leasable.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the flow of goods is a crucial aspect of supply chain management and logistics. It refers to the movement of products from the point of origin, such as a manufacturer or supplier, to the point of consumption, such as a retail store or consumer.
A good flow can bring several advantages to a business, such as increased efficiency, reduced costs, improved customer satisfaction, increased flexibility, better inventory management, and better forecasting and planning.
To optimize the flow of goods, companies can implement a transportation management system, use warehouse management systems, implement a demand-driven approach, improve communication and collaboration with suppliers and partners, use data and analytics, and continuously monitor and measure its performance. One good tool to optimize the overall rate of return of a business is value stream mapping.
By doing so, they can optimize their supply chain operations, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction. To put it in a nutshell, the flow of goods is the backbone of any business and its optimization can lead to a better and more successful company.
Reference :
- This blog post was written with the assistance of an AI language model, specifically ChatGPT. While the model generated the initial content, it has been extensively revised, edited, and fact-checked by the author to ensure accuracy and compliance with Google’s guidelines. The author takes full responsibility for the final product and any errors or inaccuracies that may remain.