Industry 5.0 is a relatively new concept that describes an evolution of industrial manufacturing towards a more agile, automated, connected, and human-centric approach.
The first wave of industrialization (Industry 1.0) was characterized by the use of steam engines for mass production.
Then, the second wave (Industry 2.0) saw the adoption of electricity and chain production, then the third wave (Industry 3.0) was marked by the automation of processes thanks to IT and technology. ‘electronic.
Finally, the fourth wave (Industry 4.0) saw the adoption of the Internet of Things, artificial intelligence, and virtual reality to optimize production.
With Industry 5.0, smart machines will collaborate with workers to create flexible, adaptive, and personalized production. Machines will be able to process large amounts of data and make decisions in real time while being able to communicate with other machines and with employees.
Workers will have a greater role in Industry 5.0, contributing their expertise and creativity to solve problems and improve processes.
Industry 5.0 aims to reconcile the advantages of robotics and automation with the advantages of human intelligence and agility. It will make it possible to respond to changing market needs and produce personalized products more efficiently and sustainably.
What is Industry 5.0?
Industry 5.0 is a recent development in the manufacturing industry that combines advanced automation with close collaboration between machines and employees. It is considered the next stage in the evolution of the industry, after Industry 4.0.
Industry 5.0 aims to create a more agile, adaptive, and personalized production system using artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things, advanced robotics, and augmented reality to optimize production. Intelligent machines and robots collaborate with humans to solve real-time problems, improve production processes and create high-quality products.
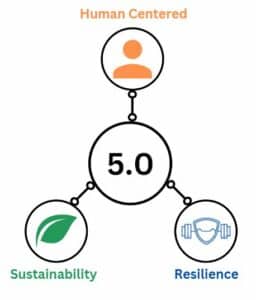
According to (Xu & al, 2021) Industry 5.0 revolves around three fundamental and interconnected values.
These values are:
- Human-centric
- Sustainability
- Resilience
What is Manufacturing Agility?
Manufacturing agility is a term that refers to a company’s ability to respond quickly and efficiently to market changes and customer demands. It involves setting up a flexible production system capable of producing a variety of products in small quantities while maintaining low costs and short delivery times.
Manufacturing agility is closely related to flexibility, as it involves the establishment of a production system capable of adapting quickly to market changes and customer demands.
Flexibility allows a company to quickly change its production process to meet specific customer demands, without affecting product quality or production costs.
However, flexibility is more oriented toward production processes, while manufacturing agility also encompasses aspects such as supply chain planning, inventory management, product design, project management, and Human Resource Management.
In other words, manufacturing agility is a holistic approach that aims to make the whole business more flexible and adaptable.
Agility VS Flexibility
An agile system is necessarily flexible, but a flexible system is not necessarily agile.
Indeed, the flexibility of a system is a technical ability to adapt to different situations, but agility goes further by integrating flexibility into an overall strategic vision to respond to changing market and customer demands.
An agile system is therefore able to react quickly to changes while maintaining high quality and low costs, and this implies a corporate culture that promotes collaboration, communication, innovation, and continuous improvement.
In other words, manufacturing agility is a combination of technical flexibility, business strategy, and organizational culture that helps to stay competitive in an ever-changing environment.
What is the Role of Humans in Industry 5.0?
The role of workers is central in Industry 5.0, as they bring their expertise, creativity, and experience to solve complex problems that machines alone cannot solve.
Employees interact with machines using intuitive interfaces, allowing for more efficient communication and optimal use of skills.
To illustrate the role of humans in Industry 5.0, let’s take the example of a car parts production plant.
In a traditional factory, machines would be used to perform the majority of production tasks, while employees would monitor and maintain the machines. However, in Industry 5.0, machines and employees work together much more closely.
In this production plant, smart machines use the Internet of Things to monitor production processes in real time and automatically adjust parameters to ensure high-quality production. Employees use intuitive interfaces to communicate with machines and monitor production processes in real time. They can also make quick changes to production processes to accommodate specific customer demands.
However, the role of employees is not limited to monitoring machines and making rapid changes to production processes. They are also responsible for solving complex problems that cannot be solved by machines alone.
For example, if a machine encounters a technical problem, a worker will be responsible for diagnosing and fixing the problem. Similarly, if a new product is to be developed, employees will be responsible for designing and developing the product using their expertise and creativity.
In sum, the role of humans in Industry 5.0 is to contribute their expertise, creativity, and experience to solve complex problems that machines cannot solve on their own while working closely with machines to optimize production.
How to Differentiate Industry 4.0 from 5.0?
Industry 4.0 introduced the digitization and automation of production processes, as well as the connectivity of machines and production systems. This has allowed better coordination between the different production processes, optimization of manufacturing processes and reduction of production costs. The machines were equipped with sensors and connected to the Internet of Things (IoT), allowing real-time data collection to monitor and optimize performance.
Industry 5.0, on the other hand, goes beyond the simple digitization and automation of production to emphasize the close interaction between workers and intelligent machines. In Industry 5.0, machines are no longer simply automated tools, but intelligent and agile collaborators who work closely with humans to optimize production and solve complex problems.
This implies that workers must have advanced skills in technology and data analysis, as well as interpersonal skills to work effectively with machines. Industry 5.0 also emphasizes manufacturing agility, which means that production processes are more flexible and can be quickly adapted to changing market demands.
In summary, Industry 4.0 introduced digitization and automation of production processes, while Industry 5.0 goes further by emphasizing close collaboration between man and machine, as well as manufacturing agility to adapt to rapid market changes.
Industry 5.0 and SMEs
Industry 5.0 can be an opportunity for SMEs to modernize and remain competitive in the market. However, it can be difficult for SMEs to embark on digital transformation, due to the high costs and complexity of the technologies associated with Industry 5.0. Here are some examples of how Industry 5.0 can fit into the SME:
- Automation of tasks: SMEs can start by automating certain tasks in their production process using robots, sensors, and control software, which can be less expensive than more sophisticated stand-alone machines. This can improve business efficiency and productivity while reducing labor costs.
- Using the Internet of Things (IoT): SMBs can use sensors and IoT devices to monitor their production processes in real time, improve product quality and reduce machine downtime. It can also help detect quality defects more quickly and prevent machine failures.
- Use of data analytics: SMEs can use data analytics to optimize their production processes, predict market trends and improve product quality. This can help SMEs make more informed decisions and adapt their products according to market needs.
- Worker training: To successfully integrate Industry 5.0, SMEs must train their workers in the use of new technologies and production systems. This can require investments of time and resources for SMEs, but can also improve the skills and motivation of workers, which can translate into better productivity and higher quality of work.
Above all, before starting a digital transformation, any company must master its processes. As they say, “We don’t automate chaos”. To do this, Lean is still relevant.
Once we have standardized our processes and eliminated waste (non-value-added operation), then we can think about automating our process. Otherwise, we would be automating our non-value-added operations and our digital transformation projects would have a high risk of failure.
In order to standardize, control, and target the processes to be improved through digital transformation, value chain mapping remains the tool of choice!
Recently, during the CNIMI symposium on digital transformation, the consensus of experts still revolved around Lean and the analysis of the value chain to improve its processes before initiating its digital transition. You cannot skip a step. Companies that have fallen behind in their digital transformation must start by controlling their “paper” process before starting to automate all the processes.
Starting with “quick wins” also makes it possible to dispel workers’ reluctance to change and begin their transition to industry 5.0 on the right foot. Anyway, trying to automate your entire business at the same time requires far too many human and financial resources!
How to Integrate Industry 5.0 in Business – From Theory to Practice?
Integrating Industry 5.0 into business may seem complex, but there are key steps that can help move from theory to practice. Here are some recommendations for integrating Industry 5.0 in a business:
- Assess needs and goals: Before beginning any onboarding process, it is important to assess business needs and goals. This can include identifying key areas that could benefit from adopting Industry 5.0 technology, as well as defining specific business goals for efficiency, productivity, and innovation.
- Set up a dedicated team: The integration of Industry 5.0 requires a dedicated team that includes professionals from different fields, such as technology, production, management, and communication. This team must be able to work together to implement the various stages of integration.
- Investing in technology: To integrate industry 5.0 in business, it is essential to invest in the appropriate technologies. This can include smart sensors, control, and automation systems, data analysis software, and communication technologies.
- Train staff: Adopting Industry 5.0 technology requires training for company staff. This can include training in the use of technology, as well as raising awareness of the importance of data security and privacy.
- Build partnerships: Industry 5.0 is closely linked to the industry ecosystem, so it is important to build partnerships with suppliers, customers, and universities to access advanced technologies, knowledge, and additional resources.
The first step is to target a process or task that is profitable to “digitize”. To do this, the analysis of the value chain remains an extremely relevant tool.
As mentioned before in the text, it is important to have previously standardized and optimized the process to be automated. In this way, we ensure the success of the project and we reduce the implementation costs since we make sure to automate only the value-added tasks.
Finally, I recommend using the “Effort/impact” matrix to target “quick wins” and start your digital transition on the right foot!
Conclusion
In conclusion, Industry 5.0 is a major evolution of the manufacturing industry that integrates advanced technologies such as AI, IoT, robotics, and augmented reality to create more efficient, more personalized, and more efficient production systems. agile.
This new paradigm is based on three fundamental values: “Human-centered”, “Sustainable development” and “Resilience”.
Manufacturing agility is essential for success in Industry 5.0, as it allows companies to quickly adapt to market changes and customer needs.
To integrate industry 5.0 in business, it is important to follow a structured methodology, involving the entire company and identifying areas for improvement to ensure a successful transition.
It is important to start with a thorough assessment of the existing infrastructure and business processes to determine areas that need improvement or modernization.
This can include the adoption of advanced technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and augmented reality (AR), as well as the implementation of new production strategies, supply, and logistics.
It is also important to involve all company employees, from the management team to production workers, in the transition to Industry 5.0. Adequate training must be in place to enable all employees to understand new processes, technologies, and communication systems, and how to use them effectively.
To continue, to ensure successful integration of Industry 5.0, the company must have a clear vision of what it wants to achieve and the benefits it wants to derive from it. This can include product quality improvements, efficiency and productivity gains, and long-term competitive advantages. With a clear strategy, a structured methodology, and the involvement of all employees, a company can successfully integrate Industry 5.0 and reap the benefits of the digital transformation of the manufacturing industry.
Finally, we have to conclude that the role of humans is essential in Industry 5.0. While in Industry 4.0 machines were designed to work autonomously, in Industry 5.0 workers are at the center of production processes and work closely with machines.
Advanced communication systems and augmented reality technologies allow employees to work more efficiently, solve complex problems and make informed decisions.
Workers are also essential to guarantee product quality and ensure agile and personalized production.
Reference :
- Abdulnour, S., Baril, C., Abdulnour, G., & Gamache, S. (2022). Implementation of Industry 4.0 Principles and Tools: Simulation and Case Study in a Manufacturing SME. Sustainability, 14(10), 6336.
- Xu, X., Lu, Y., Vogel-Heuser, B., & Wang, L. (2021). Industry 4.0 and Industry 5.0—Inception, conception, and perception. Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 61, 530-535.
- This article was written with the help of an AI language model, ChatGPT. Although the template generated the initial content, it was extensively reviewed, edited, and checked by the author to ensure accuracy and compliance with Google guidelines. The author takes full responsibility for the final product.
Author :