In the fast-paced world of the 21st century, innovation is not just a luxury—it’s a necessity. As markets evolve and technologies advance, businesses that remain static risk obsolescence. So, how do companies foster an environment that breeds innovation? Let’s dive in.
What is Innovation, Really?
Innovation is the process of introducing something new or different. It’s a way to expand and improve existing products, services, and processes while also creating new ones to solve existing problems or satisfy changing customer needs.
An innovation approach is one that revolves around bringing fresh ideas and solutions into the workplace, in order to continually look for ways to make improvements, develop new products, increase efficiency, and ultimately create value for the organization.
At its heart, innovation is the transformative process of introducing the new or optimizing the old. Whether it’s refining existing products, developing groundbreaking services, or streamlining processes, innovation addresses and anticipates changing customer needs. It’s a dynamic force that propels organizations beyond traditional practices, fostering change and growth.
In this article, two sources and four types of innovation will be covered.
For information about technological innovation, here is an interesting article: https://collectionfinance.com/en/technological-innovation/
Also, here is an article about Analytical Innovation.
Sources of Internal Innovation
Internal innovation is the use of internal resources within the organization to create new products and services or improve existing ones.
Every employee is a potential goldmine of innovative ideas. These internal insights can sprout from regular brainstorming sessions, cross-departmental collaborations, or even casual coffee break conversations.
- Spotlight Example: Companies like Google have reaped the rewards of promoting “20% time”, where employees can explore passion projects outside of their regular responsibilities.
Organizations can foster this culture by encouraging open dialogue, ensuring that employees across all levels feel safe and valued when contributing ideas. Investing in resources and incentivizing innovative thinking can further cultivate this environment.
Sources of External Innovation
External innovation is the external sourcing of ideas, solutions, and technologies to develop new products or services or improve existing ones.
It isn’t confined to a company’s four walls. This includes tapping into research institutes, being attuned to competitor strategies, or leveraging open-source platforms like GitHub.
- Spotlight Example: The open-source movement has birthed solutions like the Android OS, which powers millions of devices worldwide.
By harnessing both internal and external sources, businesses can stay ahead of market trends, ensuring they deliver what customers truly desire.
Leveraging Sources of Innovation for Business Growth
Once sources of innovation have been identified, companies must be able to leverage them for business growth. To do this, organizations should create an innovation roadmap that outlines the process for taking an idea from conception to execution.
This roadmap should include steps such as research and analysis, prototyping and testing, and implementation.
Additionally, businesses should have a dedicated team responsible for driving innovation in order to keep ideas flowing and ensure their success.
Types of Innovation
There are several types of innovations. For example, there is incremental, adjacent, disruptive, and radical innovation.
Incremental innovation involves making small changes to existing products and processes, while adjacent innovation involves slightly more radical changes that expand a product’s capabilities.
Disruptive innovation is more dramatic in nature and often results in completely new types of products or services that can disrupt the market.
Finally, radical innovation involves major transformations in technology or business models that have the potential to change an industry. It is especially important for businesses that want to stay ahead of the competition and remain relevant in a rapidly changing market.
For example, radical innovation has been used to create new products such as the iPhone or Tesla Model 3, and new business models that have completely changed entire industries, such as Amazon’s online retail business model.
Definition of Idea
An idea is a thought or suggestion as to a possible course of action. It can be for a product, solution, project, or concept. Ideas can come from anywhere and anyone at any given time. Ideas are the starting point of innovation. They spark creativity and inspire people to think differently and come up with something new that could benefit society as a whole.
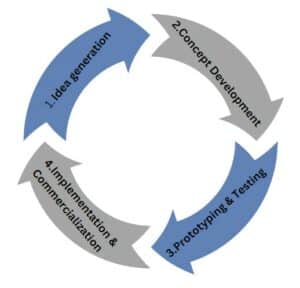
From Thought to Reality: The Innovation Process
Innovation isn’t just about having a bright idea; it’s about bringing it to life. This journey encompasses:
- Idea Generation: Brainstorming and collating diverse thoughts.
- Concept Development: Evaluating ideas against market needs and feasibility.
- Prototyping & Testing: Turning concepts into tangible prototypes to understand their real-world application.
- Implementation & Commercialization: Launching the refined product or process.
Innovation is a continuous process that evolves with changing times, challenges conventional thinking, and drives progress forward in an ever-adaptive world.
Every idea can generate a new one, sparking a chain reaction of creativity and progress. This domino effect of inspiration can lead to groundbreaking solutions, even in areas seemingly unrelated to the original concept.
It’s this interconnected web of ideas that has fueled humanity’s advancements, proving that one thought, however small, has the potential to reshape industries, cultures, and the world as we know it.
The Symbiotic Relationship Between Innovation and Technology
Innovation and technology are the yin and yang of modern-day progress. While innovation provides the vision, technology offers the tools. Breakthroughs like artificial intelligence (AI) and blockchain don’t just support innovative ventures—they inspire them.
For instance, AI’s ability to automate tasks and discern patterns has revolutionized sectors from healthcare to finance. Blockchain, with its promise of secure, transparent transactions, is redefining trust in the digital age.
Conclusion
In a world where change is the only constant, innovation is the compass that guides businesses to success.
By continuously seeking inspiration, both internally and externally, and by marrying innovation with technology, organizations can not only meet but often exceed market expectations.
Here are other articles about Innovation: